The railway industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by the need for high efficiency, reduced emissions and enhanced passenger experience, and the growing importance of technologies such as automation, advanced train control and signalling, and smart monitoring and surveillance systems.
In the last three years alone, there have been over 46,000 patents filed and granted in the railway industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in Railway: Aerodynamic rail vehicle body.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilising and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
More than ten innovations will shape the railway industry
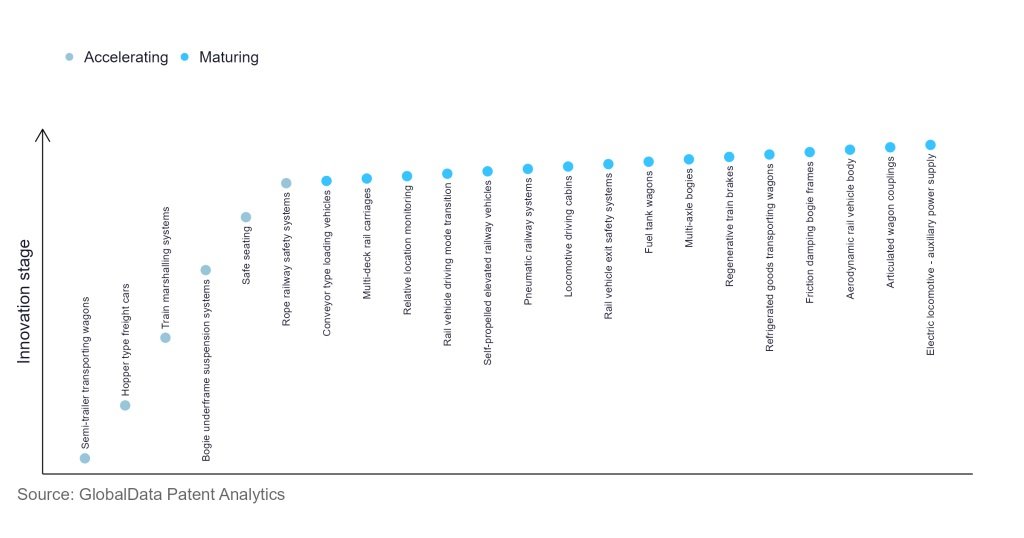
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the railway industry using innovation intensity models built on over 9,000 patents, there are more than ten innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Semi-trailer transporting wagons, hopper-type freight cars and train marshalling systems are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing.
Among maturing innovation areas are conveyor-type loading vehicles and relative location monitoring, which are now established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for the railway industry
Aerodynamic rail vehicle bodies are a key innovation area in railway
Advanced aerodynamic design plays a decisive role in improving the energy and operational efficiency of locomotives and rolling stock.
It helps in mitigating the impacts of aerodynamic drag and pressure variations on trains in crosswinds and at high speeds. Aerodynamic rail vehicle body also reduces noise and vibration and eases pressure pulses and waves caused by trains passing in the open air and through tunnels.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies.
According to GlobalData, there are 20+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established railway companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of aerodynamic rail vehicle bodies.
Key players in aerodynamic rail vehicle body – a disruptive innovation in the railway industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent and broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Patents related to aerodynamic rail vehicle bodies
Siemens is the leading patent filer in aerodynamic rail vehicle bodies. It filed patents related to floor pan, bogie structure. shallow tray-shaped base, diaphragm plates in inter-coach spacings, side walls and roof designs aimed at enhancing the aerodynamic performance of high-speed trains.
The company’s Velaro family of high-speed trains feature advanced technology in aerodynamic profiling, energy management and noise reduction. Velaro Novo is Siemens’ new high-speed train that can run at a speed of more than 300km/h and uses 30% lesser energy than the previous Velaro models. The new train features full housing of the bogies, along with streamlined front surface and inter-car gangways, and completely covered high-voltage roof equipment to further improve the aerodynamics.
Other leading innovators in the aerodynamic rail vehicle body design space include CRRC Group, Bombardier, and Hitachi.
In terms of application diversity, Airbus leads the pack, followed by ArianeGroup and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. By geographic reach, Kawasaki Heavy Industries is the leading company, followed by Dellner Couplers and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries.
To further understand the key themes and technologies disrupting the railway industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Railway.
GlobalData, the leading provider of industry intelligence, provided the underlying data, research, and analysis used to produce this article.
GlobalData’s Patent Analytics tracks patent filings and grants from official offices around the world. Textual analysis and official patent classifications are used to group patents into key thematic areas and link them to specific companies across the world’s largest industries.